Unlike copper power cables where loss due to electric resistance of the cable itself is inevitable, the superconductive state where electric resistance becomes zero at the extreme low temperature of -196℃ has been incorporated into this product. Therefore, energy loss is minimized and large-scale power transmission and distribution is enabled. This is where it gets its nickname as “the dream cable”. LS Cable & System successfully developed AC products in 2004 following Denmark, the US and Japan. In 2013, LS Cable & System developed DC products for the first time in the world. Currently, we are the only company in the world that owns both AC and DC superconductor technology.

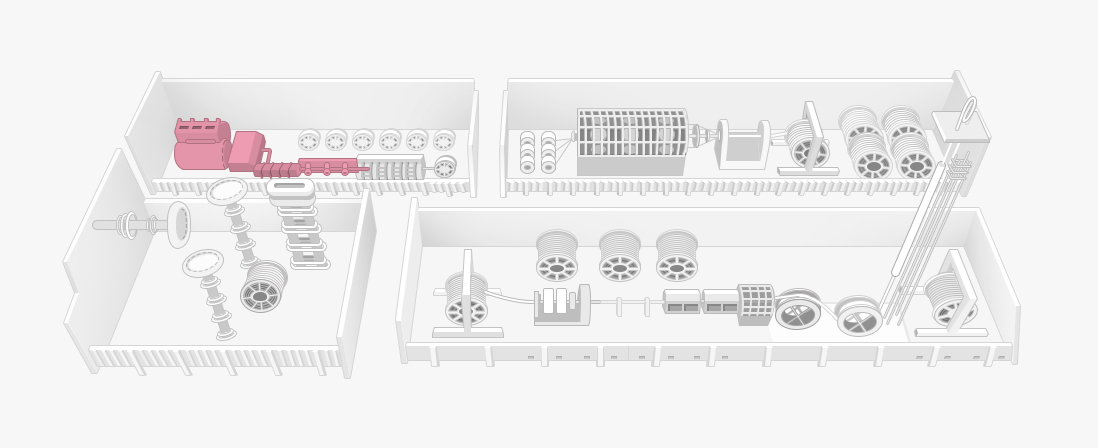
The drawn wires of 2~3mm diameter are twisted into a diameter of 15~40mm.

This is one of the most important processes for superconductive cables. The insulator PPLP is wound on the upper part of the conductor, and also the superconductive shield layer for self-shielding.
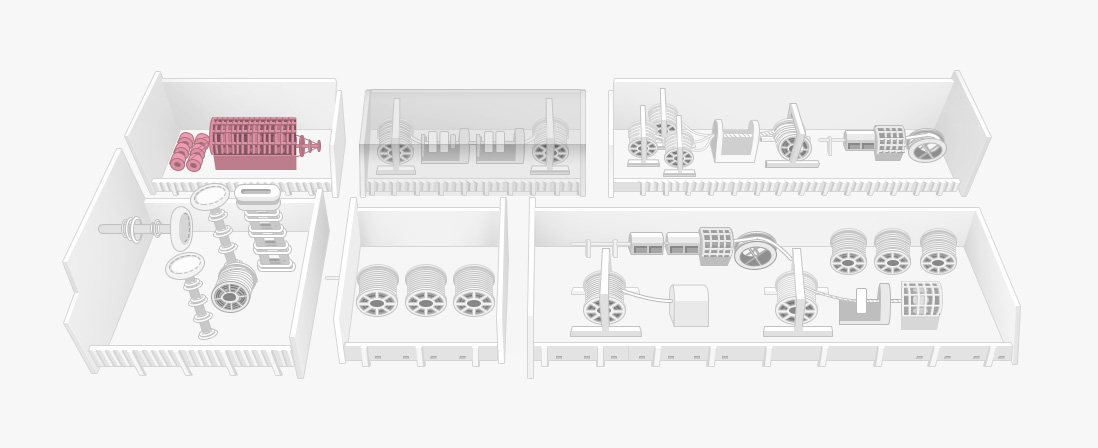
The conductors produced in the prior process are integrated into a single conductor.
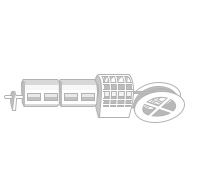
To maintain the superconductivity of the allied conductor, the liquid nitrogen circulation mold is transformed into metals such as aluminum or stainless steel through high-temperature extraction and welding.
The MLI tape and thermal spacer are produced respectively to block convection and conductive heat in the nitrogen mold.
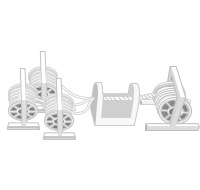
To reduce the loss of convection heat in the insulating layer, which is the last element of heat transmission, the vacuum mold is transformed into metals such as aluminum or stainless steel through high-temperature extraction and welding.
The metal sheath is enclosed once again in PVC or PE. Once again, the materials are molded at high pressure and coated at high temperature.

The material is then put into a drying room at 70℃~80℃ where vacuum exhaustion commences simultaneously.
Strict inspection is required before shipment as superconducting cable defects cause dangers.
Extra-high voltage cables are cables of 220kV~345kV used for transmitting power from generators. They must be durable enough to handle high voltage while also minimizing loss. LS Cable & System provides customers with various ultra-high voltage cables of global standard.
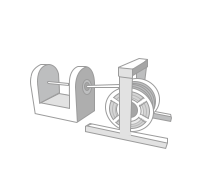
Copper(Cu) raw materials are put into the smelting furnace and extracted in cylinders of 8~9mm in diameter.
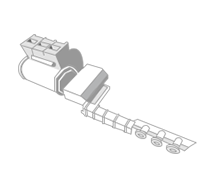
The finger-sized wires from the SCR process are then formed into smaller diameter.
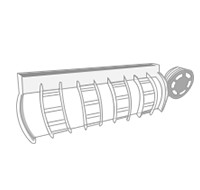
The wires are then stranded into an overall diameter of 10~60mm.
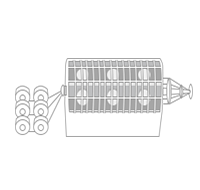
In case of segmental construction conductor, a number of individually stranded conductors are stranded together.
This is one of the most important processes for XLPE cable production. To ensure that electricity does not leak, the XLPE is extracted at high temperature and pressure and sheathed, then it is cross-linked and cooled.
The conductor is enclosed with insulation material and the exterior covered with aluminum or lead (Pb) using high pressure and temperature.
The metal sheath is enclosed once again in PVC or PE. Once again, the materials are extruded at high pressure and coated at high temperature.
Strict inspection is required before shipment as extra-high voltage cable defects cause dangers.
A fiber-optic communication system converts electric signals to light signals then transmits the signals through optical fiber. It is superior in data transmission, with a broader band compared to other communication cable systems. It is both smaller and lighter in size and weight, thus reducing the size of cable diameter. It is immune to magnetic field and electrical interferences by using light.
Fiber optic raw material in the form of a glass rod composed of a core and cladding.

The preforms are softened in the furnace and drawn to the thin glass fiber of 125㎛ diameter. The glass fiber is coated with 245㎛ of resin for protection against moisture and external shock and then coated fiber is cured through UV oven.
It is a mechanical tensile strength testing process to ensure a long-term reliability of drawn fibers.
The optical fibers are coated with 12 colors for identification.
The purpose of tubing is to protect the optical fiber against the stress during cabling or cable installation and operation.
Unwinded optical fibers from bobbin are filled with jelly and coated with plastic tube and through the cooling trough and winded again on bobbin

SZ stranding process is that of accumulating plenty strands of produced tubes. Tubes are arranged around central strength member with SZ direction. Water blocking tape or jelly are used for satisfying the water penetration.
Sheathing process is to protect the cable core from external force after or during installation.
The stranded core is coated with PE, LSZH and Nylon.
Products are strictly tested to meet a customer’s requirement. There are so many test items. For optical characteristics, there are attenuation, PMD, mode-field diameter, cut-off and so on. For mechanical and environment characteristics, there are twist, temperature cycling, impact, crush and so on.